Eye Cancer
26 January 2023
Retinoblastoma is a type of pediatric cancer that develops in the retina of the eye. The retina is located at the back of the eye. It has layers of cells that sense light and send information to the brain.
Retinoblastoma almost always develops in children under the age of 5. Treatments for retinoblastoma include cryotherapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery. The prognosis depends on several factors, such as the size and location of the tumor, and whether the cancer has spread. If the tumor has not spread beyond the eye, most children with retinoblastoma live cancer-free after treatment.
Most often, one eye is involved. In about a quarter of cases, it affects both eyes.
Retinoblastoma is caused by a genetic mutation. The causative gene is called RB1. The mutation causes the eye cells to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. In about 40% of cases the child inherits the RB1 mutation from a parent (hereditary retinoblastoma), in the remaining 60% the genetic change occurs spontaneously.
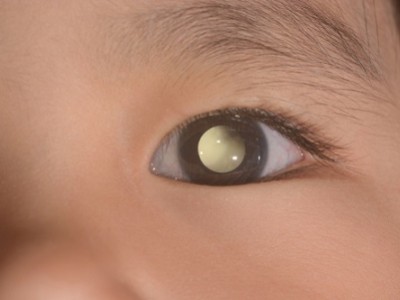
In most cases, the first sign of retinoblastoma is a change in the appearance of the eye. Symptoms may affect one eye or both, and include:
- White pupil (leukocoria): this is usually the first sign of retinoblastoma. The pupil (the round, black center of the iris) may appear white at certain angles or in a flash photo (pupils often appear red in a flash photo).
- Crossed eyes (strabismus): The eyes may appear misaligned, or one eye turns in a different direction than the other. Strabismus can be mild to severe.
- Red or inflamed eyes -- inflammation and irritation may appear anywhere in the eye. The eyes may be painful or tender.
It is not possible to prevent non-hereditary retinoblastoma.
If you or your partner had retinoblastoma as a child, you have a 50% chance of passing the disease on to your children. If you have a family history of retinoblastoma or have the RB1 gene mutation, you may consider genetic testing before having children. Children with a family history of retinoblastoma should have regular eye examinations starting at birth. Early detection and diagnosis is very important. Early diagnosis can significantly improve the prognosis and can prevent vision loss.
At the center we have pediatric ophthalmologists and retinologists for the detection and treatment of retinoblastoma. Request your appointment here.











