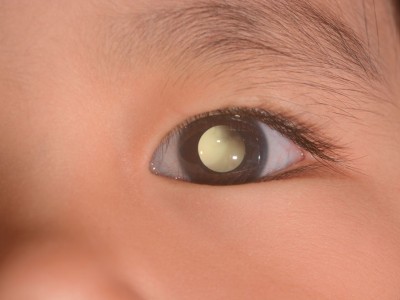
What is leukocoria in children?
27 January 2022
Leukocoria means "white pupil" and appears due to light reflections produced by certain intraocular lesions that usually manifest in childhood, when there is direct lighting.
Leukocoria in children is always a worrying clinical symptom because, in 50% of cases, it indicates the presence of advanced retinoblastoma (the most common malignant intraocular tumor in children).
Generally, the closest relative to the child is the one who usually first detects this clinical symptom, either by direct observation or by the appearance of pupillary reflexes in photographs taken with a flash.
Fortunately, leukocoria is not always indicative of a malignant process, it can also accompany other congenital disorders (cataracts, persistent fetal vascularization syndrome, congenital anomalies of the optic nerve, persistence of myelin fibers); parasitic infections (toxocariasis); vascular pathologies of the retina (Coats disease); neonatal diseases (retinopathy of prematurity), among others.
Retinal tumors present in neuro-oculo-cutaneous syndromes, such as Bourneville's tuberous sclerosis or von Recklinghausen's neurofibromatosis, may also be associated with leukocoria, although they are less frequent.
In these cases, early diagnosis is crucial, and a specialist ophthalmologist should be consulted immediately to determine the exact cause of this anomaly and the most appropriate treatment for the correct restoration of vision.
In other cases, it is essential to examine the child in the operating room under anesthesia, to be able to visualize in detail all the structures inside the eyeball.
The most widely used complementary test for the investigation of leukocoria is high-resolution ultrasound. With the help of ultrasound we can confirm the presence of calcifications (typical of retinoblastoma), the persistence of embryonic structures and rule out retinal detachment easily and quickly.











